ESG as a Strategic Tool for Long-Term NGO Stability.
Sustainable development for NGOs refers to the capacity of a non-governmental organisation (NGO) or a charitable foundation (CF) to operate effectively and consistently over the long term, even in a changing environment.
It encompasses more than just financial sustainability (i.e., access to resources). It also includes professional management, transparency, team development, programme effectiveness, and trust from society and partners. In other words, NGOs and CFs that embrace sustainable development are not dependent on a single grant or project. Instead, they establish systemic operations that generate long-term impact.
One of the modern pathways to achieving sustainability for NGOs is the adoption of the ESG approach. Implementing ESG demonstrates an organisation’s responsibility, transparency and commitment to long-term values. In today’s climate, an increasing number of donors, companies and international institutions assess potential partners through the lens of ESG. Organisations that adopt the ESG principles and report on them are more likely to attract funding, build long-term partnerships and launch joint initiatives.
In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of how NGOs can implement the ESG approach.
Anastasiia Skok, Head of ESG at BDO in Ukraine, presents her professional insights on the relevance of sustainable development for nonprofit organisations, the benefits of ESG reporting and the practical aspects of ESG implementation.
-
Why is ESG increasingly relevant for nonprofit organisations?
Firstly, there is an increasing demand from the public for transparency and accountability, especially for organisations that receive funding from donors and work in areas of social impact. Implementing ESG helps to demonstrate adherence to the principles of sustainable development, which increases public trust.
Secondly, ESG is becoming a key factor in attracting funding. Donors and international partners are increasingly evaluating not only financial indicators but also the environmental, social and governance practices of organisations. Implementing ESG can improve an NGO’s chances of receiving grants and forming partnership projects.
Notable trends in sustainable development for NGOs in Ukraine and worldwide include the tightening of reporting regulations in the EU, the integration of ESG into strategic planning and the increasing popularity of business collaborations based on social responsibility principles.
-
What is the present situation with ESG reporting for nonprofit organisations?
The Association of Sustainable Development Experts (ASDE), for example, became the first public organisation in Ukraine to prepare an ESG report in accordance with the GRI and SASB reporting principles. The report, which covers the organisation’s activities for 2023, is available on the official ASDE website. A new report for 2024 has already been released.
However, the main barriers to the implementation of ESG reporting among NGOs include a lack of funding for developing and maintaining reports, a shortage of qualified personnel with ESG competencies and the absence of clear, sector-specific methodological guidelines and standards.
The demand for ESG reports from donors and partners in Ukraine is gradually increasing. An increasing number of grantmakers are including sustainability requirements in their funding conditions, thereby encouraging NGOs to adopt ESG practices.
-
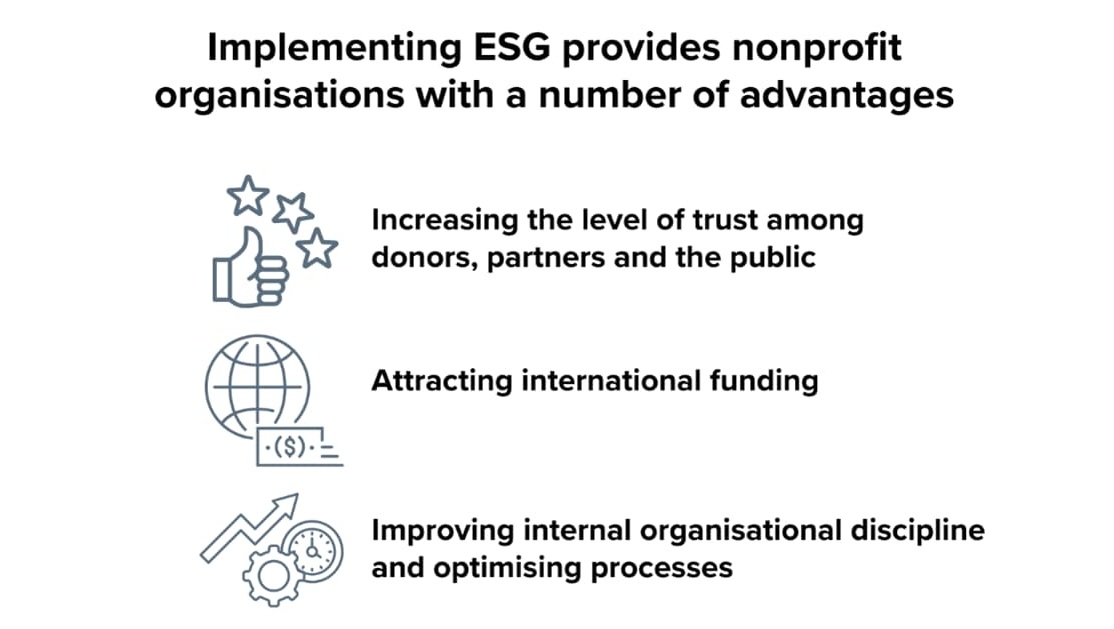
What are the benefits of ESG for nonprofit organisations?
Secondly, ESG reporting facilitates access to international funding, since most global donors and funding platforms now regard sustainable development as a fundamental criterion for supporting projects.
Additionally, adopting ESG approaches fosters internal organisational discipline and process optimisation, enhancing the overall efficiency of NGO operations over time.
-
What does the practical implementation of ESG in NGOs entail?
Key ESG indicators for NGOs include:
• level of environmental impact (e.g. emissions, resource consumption)
• social initiatives and outcomes,
• gender equality indicators
• community engagement
• transparency in financial and managerial activities.
For practical ESG implementation, it is important for NGOs not only to define areas of impact, but also to develop an internal strategy or policy aligned with the organisation’s mission and values. At the initial stage, it is advisable to appoint a designated individual or a small team to coordinate the ESG direction, as well as to establish a system for collecting and monitoring data on key indicators. This helps structure the approach and avoid a formal attitude toward reporting.
Special attention should be paid to selecting the tools and standards that the organisation will adhere to. NGOs can adopt international practices, such as the Sustainable Development Goals or GRI standards, adapting them to their own scale and areas of activity. External experts or partners with ESG experience can be involved to assist with methodology, if needed.
Communication is also a crucial component. Regular publication of ESG reports in open access, integration of relevant indicators into grant applications and donor reporting, increases trust among both partners and the community. This approach demonstrates transparency and accountability, significantly strengthening the organisation’s reputation.
Integrating ESG into the operational practices of public organisations also brings internal benefits. It promotes process optimisation, more efficient use of resources and the development of a culture of responsibility within the team. This approach not only fosters collaboration with donors and international partners, but also strengthens the organisation’s overall resilience.
-
What experience do international nonprofit organisations have in implementing ESG principles?
These organisations report on the social impact of their programmes and adhere to high environmental standards and strict governance practices, including anti-corruption measures, financial transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Their experience demonstrates that integrating ESG not only enhances reputation, but also enables effective risk management, resource optimisation, and the attraction of long-term partners and donors who prioritise sustainability and transparency.
For many international NGOs, ESG reporting has evolved from a mere formality into a core component of their development strategy, offering them a competitive advantage on a global scale.
-
What practical advice can help nonprofit organisations prepare for ESG reporting and what are its benefits?
To effectively implement ESG reporting, a nonprofit organisation should follow several practical steps:
- Readiness assessment and internal audit. Analyse current processes and identify existing data on the organisation’s environmental, social and governance impact.
- Defining key ESG indicators. Select indicators relevant to your activities, including resource consumption, emissions, social programs, gender policy and governance transparency.
- Policy and procedure development. Introduce internal documents regulating ESG approaches: code of ethics, environmental policy, gender equality policy, etc.
- Staff training. Ensure staff receive ESG-related training and appoint responsible individuals.
- Data collection and analysis. Establish systems for regular data collection, verification and analysis for reporting purposes.
- Report preparation. Use international sustainability standards adapted to the nonprofit sector.
-
What ESG reporting regulations and standards exist for NGOs?
• GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) — the most widely used standard for preparing sustainability reports, covering environmental, social and governance aspects.
• SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board) — standards that help organisations disclose sustainability-related information in financial reporting.
• ESRS (European Sustainability Reporting Standards) — European sustainability reporting standards developed to improve transparency and the quality of sustainability information within the EU. They aim to help organisations align with the European Union’s sustainability requirements.
• UN SDGs (United Nations Sustainable Development Goals) — a reference point for identifying priority areas of impact.
• ISO 26000 — an international standard on corporate social responsibility.
• Ukrainian legislation — it is important to consider laws related to reporting, environmental protection, labour relations, anti-corruption measures and regulations governing the activities of nonprofit organisations.
-
What opportunities and prospects exist for ESG development among NGOs?
ESG presents novel prospects for NGOs to partner with businesses and international foundations, which are progressively guided by social responsibility and sustainable development when selecting partners.
It is anticipated that the demand for ESG reports among Ukrainian nonprofit organisations will increase in the coming years, driven by stricter donor requirements, the strengthening of international standards and the overall trend towards sustainability.
In the long term, developing ESG principles within NGOs will strengthen trust among donors and partners and enhance the institutional capacity of the sector itself. The systematic application of ESG approaches will help Ukrainian organisations to integrate into the global sustainability context, increase their international competitiveness and establish themselves as influential participants in their country’s recovery processes. Therefore, ESG is not just a temporary trend for NGOs, but a strategic direction that will define their future role and effectiveness.
If your nonprofit organisation requires advice on sustainable development or ESG reporting, please contact BDO in Ukraine. Our experts will help you select the most suitable solutions and ensure the effective implementation of ESG for your organisation.
The expert questions were prepared by Victoria Silchenko, Senior Business Development Specialist, Head of the NGO Industry Group at BDO in Ukraine.